2022-06-07 Support Views 577
What are VOCs, VOCs and TVOCs?
VOC is the abbreviation of Volatile Organic Compound. Different countries and organizations have slightly different definitions of VOC. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) defines a VOC as any carbon compound that participates in atmospheric photochemical reactions, with the exception of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, metal carbides or carbonates, and ammonium carbonate. The European Union defines a VOC as any organic compound with an initial boiling point less than or equal to 250°C (482°F), measured at a standard atmospheric pressure of 101.3kPa. In China, VOC refers to any organic compound with a saturated vapor pressure greater than 133.32Pa at normal temperature and a boiling point of 50°C - 260°C at normal pressure, or any volatile organic solid or liquid at normal temperature and pressure.
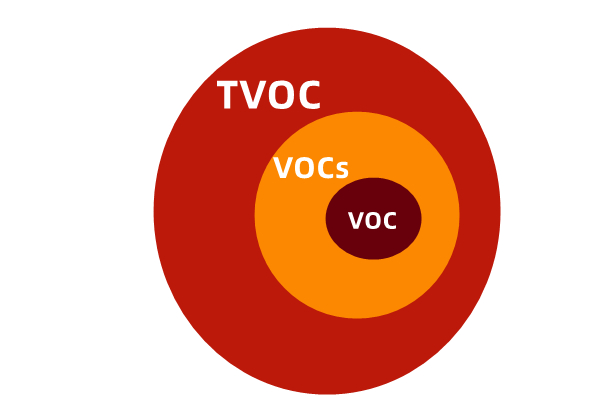
VOC and VOCs are the same kind of substances. Since volatile organic compounds generally have more than one component, VOCs are actually more accurate.
The above are definitions in the general sense. In the sense of environmental protection, VOCs refer to the active type of volatile organic compounds, that is, volatile organic compounds that can cause harm, mainly including alkanes, aromatic hydrocarbons, olefins, halogenated hydrocarbons, esters, Aldehydes, ketones and other organic compounds.
TVOC refers to total volatile organic compounds. The relationship between VOC, VOCs and TVOC is as follows: